How to Choose LED Display?
When choosing an LED display, customers often ask a lot of standard questions like “How do I decide which specifications are important?”, “What is the difference between RGB (DIP) and SMD technologies?” and others. This article will tell you what factors to consider before ordering an LED display.
In fact, LED video displays have multiple advantages. The following features enable you to use these displays for advertising purposes both outdoor and indoor:
- High contrast and brightness
- Wide viewing angle
- Playing video and graphics, displaying animation
- Setting the number of times an ad is shown
- Managing and programming online
- Time of the day and distance do not affect the working capacity
- Time of year, weather conditions and ambient temperature do not affect the working capacity
A big plus point of an LED display is its reliability and a long service life (up to 10 years). Furthermore, even if a part of it is damaged, the display will not stop working. The faulty cluster will stay unnoticeable.
How Does LED Work?
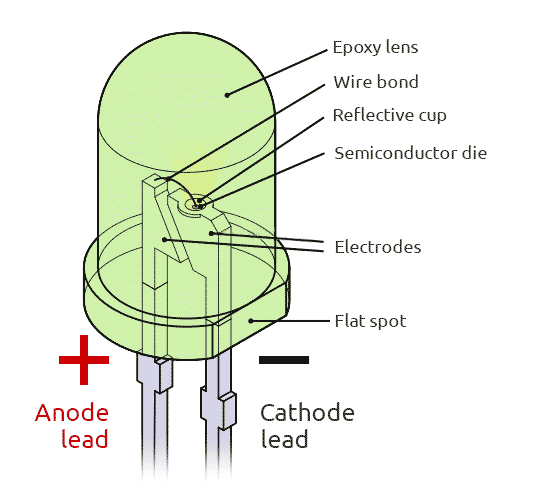
The main LED element is a semiconductor emitting light when the current passes through it. Around the LED, a reflector is located directing light in the required direction. These elements are covered with transparent epoxy coating. The coating often has a certain color: blue, green or red. This is done to enable determining the diode color without connecting.
The crystal determines the color of a diode. The crystal color depends on its chemical composition. If we change the crystal in some way, it can result in a completely different diode color. It often happens that LEDs from the same producer having the same color are different. If you place such LEDs into one display, the difference will be seen from afar.
To avoid falling a victim to such a situation, try to buy screens from big manufacturers only. These manufacturers order large batches of LEDs, thus minimizing a chance of different elements being present in the same display. Moreover, big companies often have their own make of diodes and spare parts for screens, and offer a full cycle of quality control.
LED operational lifetime does not indicate the moment when a diode finally fails; in fact, it shows when its brightness falls to 50%. This means that even after the display has finished its useful life, it will still work, but the color of images will slightly change.
LED Displays
An LED display is a screen where the image is formed by means of LEDs. A big plus point of LED displays is no "loop" effect. Besides, the number of on-off cycles does not affect their performance. What is more, under direct sunlight, images on LED displays are much better in terms of contrast and viewing angle than on other types of displays.
LED modules are elements from which LED displays are assembled. All LED displays are composed of individual modules. The larger the display, the more modules you will need for it. Each producer has its own standard size for LED panels, but if necessary, you can order non-standard size modules.
You shouldn’t confuse an LED display with an LCD display. In LCD displays, LEDs are used only for backlighting; the image is formed using an LCD matrix.
Types of LED Displays
There are three types of LED displays.

Type 1

Displays composed of groups of multicolored LEDs. Each group forms one pixel. There must be at least one blue, one red, and one green LED in the group. These three colors create the entire color spectrum. RGB displays are brighter, so they are recommended for the use outdoors.
Type 2
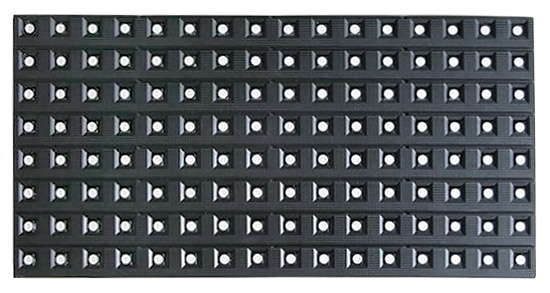
Displays of the second type are displays from SMD LEDs. LEDs of different colors are placed in one cell, which is considered one pixel. One pixel creates the whole spectrum of colors. In displays of the second type, the surface appears to be flat. SMD displays have a rather high resolution, therefore, they are recommended for the indoor use. However, there are special models that are also suitable for the outdoor use. It is worth noting that in SMD displays the decrease in brightness does not affect the color range.
Type 3
We may state that the third type is an improved type 1. Here a group of diodes includes one more LED. That is, a group consists of four diodes (RRGB): two red, one green and one blue. Displays of this type have high resolution, but they are not so bright.
Brightness
An LED screen’s brightness is measured by number of nits (cd / m2). To decide on brightness requirements, it is important to know where and under what conditions the display will be used.
Let us look at several examples of LED display use and the brightness level they need. To ensure decent display operation indoors, the screen has to be approximately 600 nits. However, for displays used outdoors, you may need a higher brightness level. For example, displays used on the street should be at least 2,000 nits. For a message on the screen to be bright and readable under direct sunlight, the display brightness should be least 6,000 nits. A display of 12,000 nits will allow you to see the picture at a great distance. The brighter the screen, the higher the audience coverage.
When choosing an LED display, pay attention to its ability to automatically adjust the brightness level at twilight.
LED Display Resolution
For an LED display, we use the phrase “pixel pitch” instead of “resolution”. A pixel pitch is a distance between the centers of neighboring pixels, SMD diodes, or groups of LEDs. The higher the screen resolution, the smaller the pixel pitch (pixels are located quite close to each other). Therefore, the act of looking at high resolution screens is comfortable even from a short distance.
To denote the pixel pitch we use letter “P”. Next to it, there is a figure indicating a distance between centers. For example, P6 is a display with the pixel pitch of 6 mm. This is a very important characteristic, because it determines the cost of the display and affects the perception images. For example, display P16 is best viewed at a distance of 16–20 meters. If you come closer, you will not get a clear image. If you go farther, small details will become invisible.
When choosing a display, you need to know where and from what distance a potential customer would look at it.
Maintenance
To maintain an LED screen, you must have access to the front or back. Front maintenance LED displays are expensive and have a complex design. Such a display can be installed as close to the wall as possible because access to its rear part is not required. Rear access screens are best used in places where there will be constant access to the rear of the screen.
How Do You Change Information On an LED Display?
All LED displays retain current display information after shutdown. To update information on the display, you need to install a special program (it comes with a display) on a computer, laptop or smartphone. You can download the video using a USB flash drive, an Ethernet network interface (RJ45), a wireless Wi-Fi network, a 3G mobile network, or remote access through a cloud service, if you need to manage multiple displays at the same time.
In addition to the programmed information, each LED display can show current time, date, as well as ambient temperature and relative humidity.
You can buy LED displays of different types at our store. Our technical support will help you find the right display and tell you how to program it correctly. In addition, the package contains parts and components necessary for assembling LED displays.
