Types of Microscopes
The history of microscopes goes back to the 16th century. The first microscope ever made by a man was optical and consisted of a set of lenses that allowed people to obtain an enlarged image of studied objects. At present, there are a great many microscopes due to the huge scientific and technological progress in all spheres of our life. These devices differ not only in their purpose, but also in their operating principle. Let's try to systematize our knowledge of modern microscopes.
Classification of Microscopes
Let’s consider the most general classification of microscopes based on the device resolution accuracy. The resolution of a microscope is its ability to produce a clear, separate image of two closely spaced points of an object. This characteristic is determined primarily by the wavelength of radiation used in microscopy (visible, ultraviolet, X-rays).
- optical (light);
- electronic (or electron);
- X-ray;
- SPM (scanning probe microscopes).
Since optical microscopes hold a special place in our review, let us leave their detailed consideration for the finale.
Electron Microscopes
An electron microscope is a super-power device that makes use of a beam of electrons to obtain an image, instead of luminous flux used by an optical microscope for this purpose. This type of microscopes is much more powerful than conventional light microscopes, and their resolution is 1000-10000 times higher.
Electron microscopes can be further divided into:
- scanning microscopes – scanning is performed with a focused electron beam under industrial vacuum conditions;
- transmission microscopes – designed to study thin objects with a beam of electrons passing through the object.
Such microscopes are complex and expensive devices; therefore, they are most often used in scientific research or at large enterprises.
X-ray microscopes
An X-ray microscope is a device for studying very small objects whose dimensions are comparable to the length of an X-ray wave. The operating principle of such a microscope is based on the use of X-rays with a wavelength between 0.01 and 10 nanometers. X-ray microscope resolution is between electron and optical microscopes.
- projection;
- reflective.
Most widely used are projection microscopes; they allow you to check the quality of thin coatings and to obtain micro X-rays of biological and botanical cross sections up to 200 micron thick. An important advantage of X-ray microscopes is that they can be used to observe unprepared live cells.
Scanning Probe Microscopes
A scanning probe microscope is unlikely to be instrumental for home use. This is a specialized class of microscopes using a special scanning probe to build an image. Thanks to this microscope, a three-dimensional image is obtained with a very high resolution (less than 0.1 nm). Currently, scanning probe microscopes have found application in almost all areas of science: physics, chemistry, biology, biochemistry, pharmaceutics, materials science, photochemistry, and other fields.
Optical Microscopes
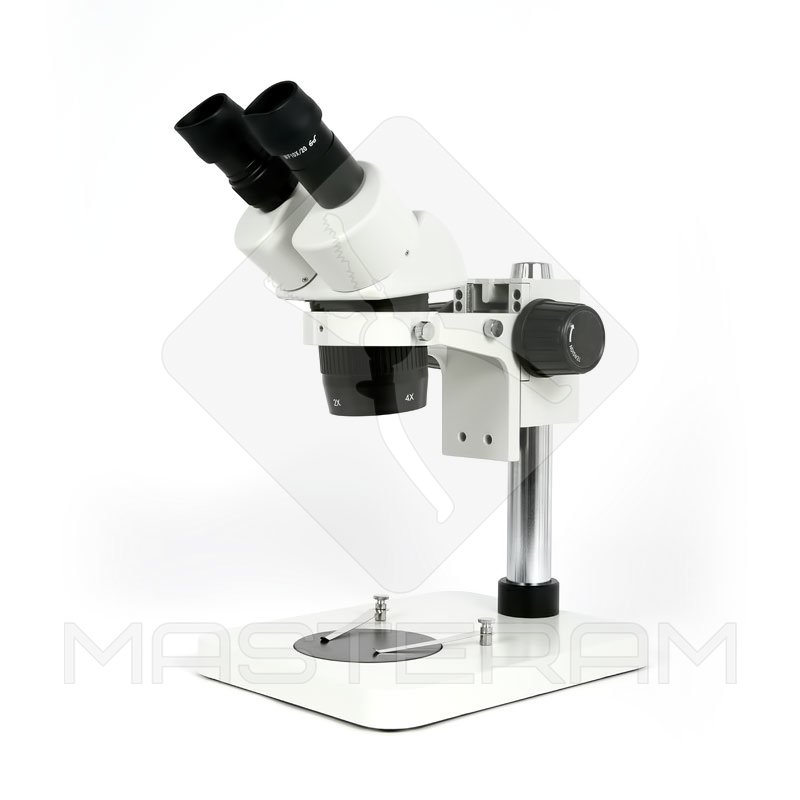
An optical (light) microscopeis the “oldest” by classification and the most widespread microscope to date. However, don’t you think that its design and capabilities have remained unchanged. A standard microscope consists of an optical system (lens, eyepiece and illumination device) and a mechanical system. The principle of operation are based on the laws of classical optics.
Optical microscopes differ in their purpose:
- Biological microscopes – microscopes of transmitted light, designed to study transparent and translucent objects;
- Stereoscopic microscopes – reflected-light microscopes with a 3D image, designed to study opaque objects;
- Metallographic microscopes – reflected-light microscopes with illumination coming from a built-in light, designed to study opaque objects;
- Fluorescent microscopes – based on the phenomenon of luminescence of objects, designed to study opaque and translucent objects with varying degrees of reflectivity.
And this is not a full list of where optical microscopes are applied.
By design, you can also divide optical microscopes into monocular, binocular and trinocular. If you need to work with a microscope for a long time, binocular and trinocular models are preferred.
Soldering Microscopes
It is no secret that a properly selected tool contributes to seamless and fast performance.
For soldering, choose a microscope with small magnification. In this case, there will be enough space between the lens and the working surface if you need to work with tweezers and a soldering iron. The ST60-24B1 binocular microscope can serve as an example. If necessary, the working distance can be increased by installing a diminishing lens on the objective (0.75x or 0.5x). The visible area of the working surface will increase in parallel.
It’s convenient when the eyepieces of a microscope are placed at an angle to the working surface.
To protect against rosin fumes and solder, use a protective glass on the objective (lens) of a microscope. It is also necessary to provide good exhaust ventilation.
A digital microscope takes a special place among optical microscopes. Professional digital microscopes are a major technological breakthrough in modern instrumentation technology. In such devices, the optical system is combined with a transforming matrix that allows you to convert the light flux into a digital signal and transmit it to a computer for further processing. Digital cameras and microscopes are provided with photo and video cameras for recording data, as well as monitors and printers for visualization. Depending on the type of image output, we can distinguish between USB microscopes and TV microscopes.
Trinocular microscopes are a combination (or symbiosis) of optical and digital microscope types. In addition to the two standard optical eyepieces, they have a third eyepiece for capturing the whole process on a special surveillance camera and displaying a digital image on the screen.
Today, due to the huge popularity of PCs, digital microscopes have been unified. Now most of them work from a standard USB port on a computer that has the appropriate software installed compatible with a particular digital microscope model. Sometimes they even use the term "USB-microscope".
Digital Microscopy
Now the digital microscope is becoming quite affordable not only for big scientific or industrial centers, but even for ordinary schools. Moreover, they have already developed the methods of the digital microscope use in biology classes, so we can soon expect the emergence of a “school” (children's) digital microscope, which is just as affordable as widespread ordinary optical models.
Digital microscopes are used in
- Quality control of manufactured products
- Tests and studies
- Analysis of the circuit board state
- Electronics repair
- Education and training (studying natural sciences, biology, chemistry)
- Hobbies and passions (working with small parts and elements)
- Collecting (coins, jewelry, stamps, and more)
- Tissue research
- Medicine (analysing the skin condition, teeth health, etc.)
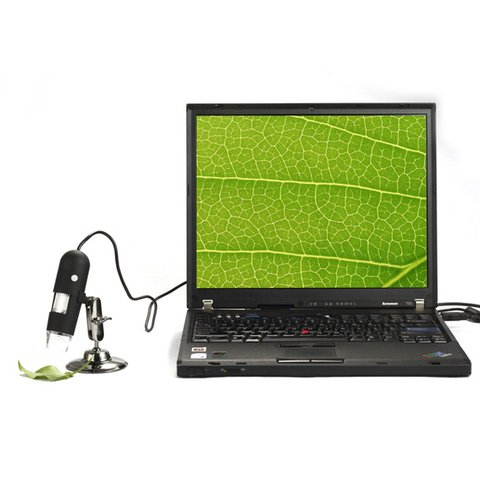

The maximum magnification in digital microscopes often exceeds that of optical microscopes, which opens up new opportunities for users. Digital technology in the most advanced microscopes also provides the ability to save video streams. To obtain the sharpest images of the best quality they use modern methods of camera focus and automatic adjustment. The issue of additional lighting is addressed by a built-in LED backlight in some models.
Digital technologies of image storing and processing simplify the process of documenting data and the issue of comparing the objects observed. Users can save the necessary images in the directories they need, and later compare the observed objects or the state of the same object in different periods of time. Thus, it is possible to carry out quality control and other tests. Saved images can be processed using external editors.
Popular Models of Microscopes
We would like to mention one of the manufacturers who produce affordable and easy-to-use digital microscopes – Supereyes. The company has successfully been engaged in developing and producing digital devices for zooming and studying objects, i.e., microscopes and endoscopes, since 2005. During this time, the company has been improving its products and expanding the range of products to satisfy the latest trends and meet market requirements. According to the manufacturer, they have world-renowned institutions and organizations, such as Samsung, Motorola, Toshiba, Huawei, Hewlett-Packard, Cornell University, etc., as clients.
 Model Range of Supereyes Microscopes
Model Range of Supereyes Microscopes
In recent years, a whole line of Supereyes microscopes has appeared. We tested them and even shot video reviews for you. Please learn more about these models below.
USB Microscopes
USB microscopes can be used to work with small objects, electronics, printed circuit boards, and other objects.
Supereyes B003+ USB Microscope
| Magnification | 300х |
| Sensor | 2 Mp |
| Interface | USB 2.0 |
Supereyes B005 USB Microscope
| Magnification | 200x |
| Sensor | 1,3 Mp |
| Interface | USB 2.0 |
Supereyes B008 USB Microscope
| Magnification | 500x |
| Sensor | 5 Mp |
| Interface | USB 2.0 |
Supereyes B010 USB Microscope
| Magnification | 400x |
| Sensor | 2 Mp |
| Interface | USB 2.0 |
